Editor’s note: This post was originally published on the nVent Rail and Transit Blog. Click below to find more industry news and specific solutions for rail.
nVent ERICO provides a variety of solutions for earthing (grounding) and bonding across many industries, including rail. Earthing systems are a critical part of railway safety, protecting passengers and the public from electrical shock by preventing electrical voltages in the network where they shouldn’t be. Railways have complex electrical infrastructures, and—in addition to public safety—robust grounding systems protect mission-critical equipment from costly damage.
Earthing is achieved using by a grounding system to achieve a low-impedance path to the earth. An earthing system must at least contain ground electrodes, conductors and connections that connect electrodes/conductors/ground bars/equipment. These components are installed in different combinations and configurations throughout the network, depending on the type of rail infrastructure application.
Earthing conductors are typically composed of either 100 percent pure copper or galvanized steel. These conventional components of earthing systems bring the familiar trade-off between economics and service life on track. With its resistance to corrosion, pure copper earthing conductors provide a longer service life on track. However, its higher cost makes it an attractive material for theft. Galvanized steel is less costly but susceptible to corrosion and must be replaced more often. For metro railways in China, the balance between material cost, performance and service life proved to be a significant challenge, which led us to introduce the nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor, an innovative ground conductor alternative that overcomes the limitations of conventional materials.
The Advantages of nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor
The nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor features a nickel-plated steel core electroplated with copper, creating a copper surface. This composition allows Cu-Bond Round Conductor to be a cost-effective alternative to pure copper with a surface that resists corrosion and a steel core that contributes to a lower overall material cost. A high-quality product that meets global electrical standards, Cu-Bond Round Conductor is UL Certified to IEC® 62561-2 (requirements for conductors and earth electrodes) and meets the requirements for IEC® 62305-3, Edition 2, Lightning Protection.
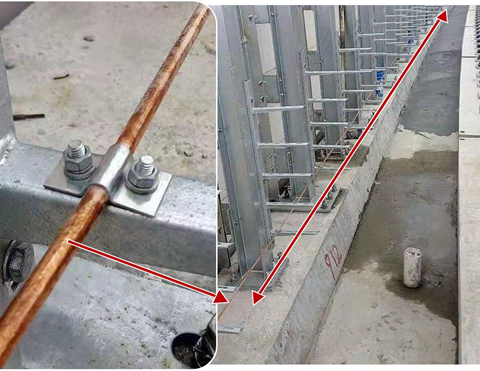
Pictured below, nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor installed above grade in a concrete slab track application in the city of Nanjing.

Introducing the nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor to Metro Railways in China
For many years, the national standard for ground conductor material in China was pure copper. For economic reasons, however, galvanized steel tape was accepted for
use in earthing systems. Faced with the typical drawbacks of galvanized steel, specifically its susceptibility to corrosion, metros throughout the region were open to a better solution.
Approximately 10 years ago, the nVent ERICO sales team in China presented metro railways with Cu-Bond Round Conductor as a cost-effective alternative to pure copper that could resist corrosion and provide longer service life than galvanized steel.
In 2012, the first installation of Cu-Bond Round Conductor was made in the city of Nanjing. In addition to providing a longer service life, Cu-Bond Round Conductor proved to be easier to install for many Chinese metros than galvanized steel because it is offered in longer increments that require fewer welds. Its corrosion-resistant properties were also ideal for the many special track structures common in metro rail such as elevated tracks and tunnels. Today, nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor is approved in 10 metros across China. This is an example of innovative nVent solutions that help our customers overcome limitations of conventional materials through products that provide cost-effective performance.
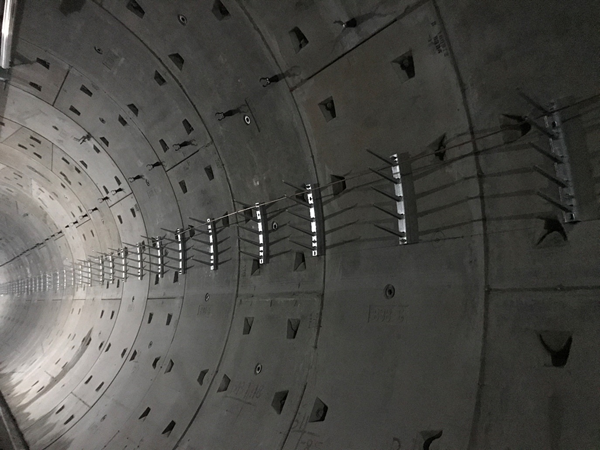
Pictured below, nVent ERICO Cu-Bond Round Conductor installed in a rail tunnel in the city of Chengdu. This application includes 120 kilometers of conductor used for signal grounding.